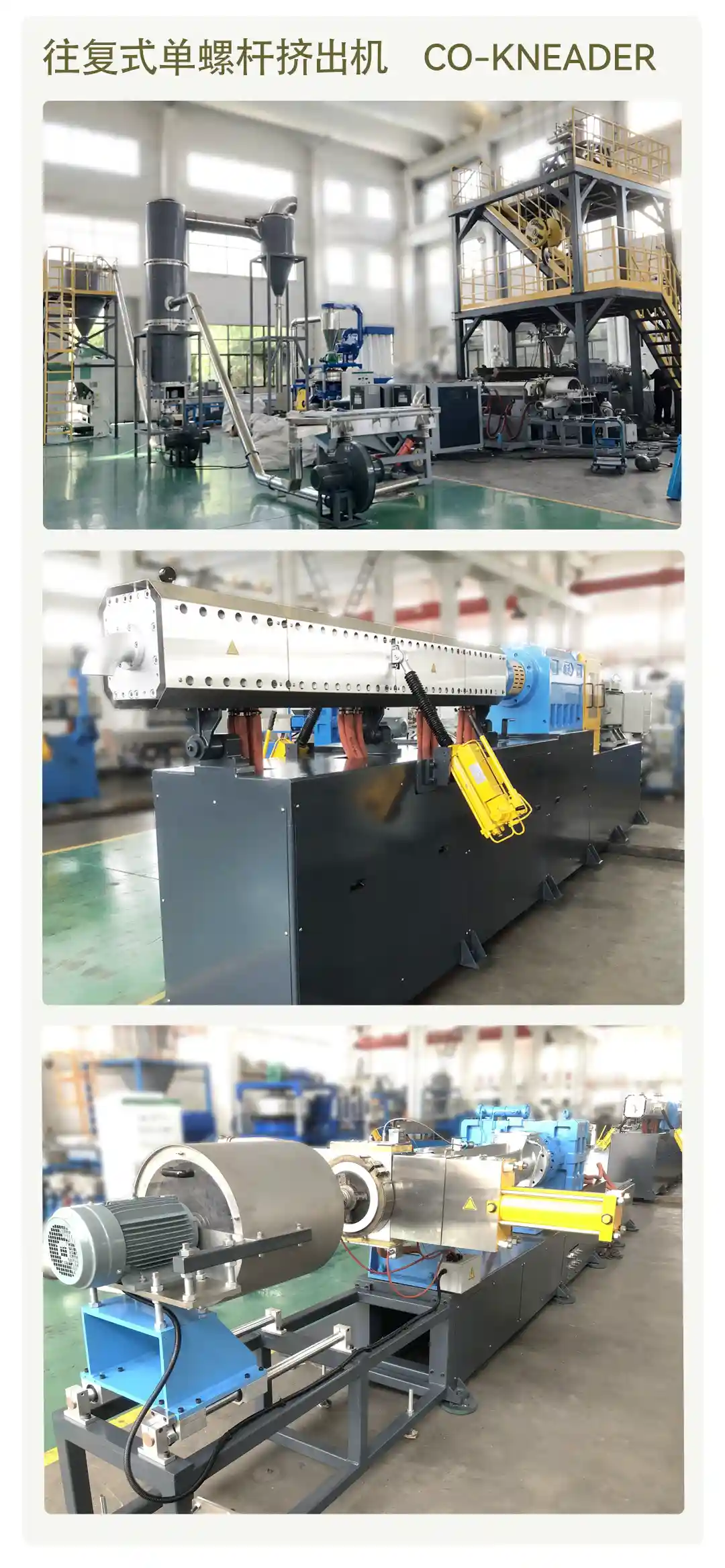
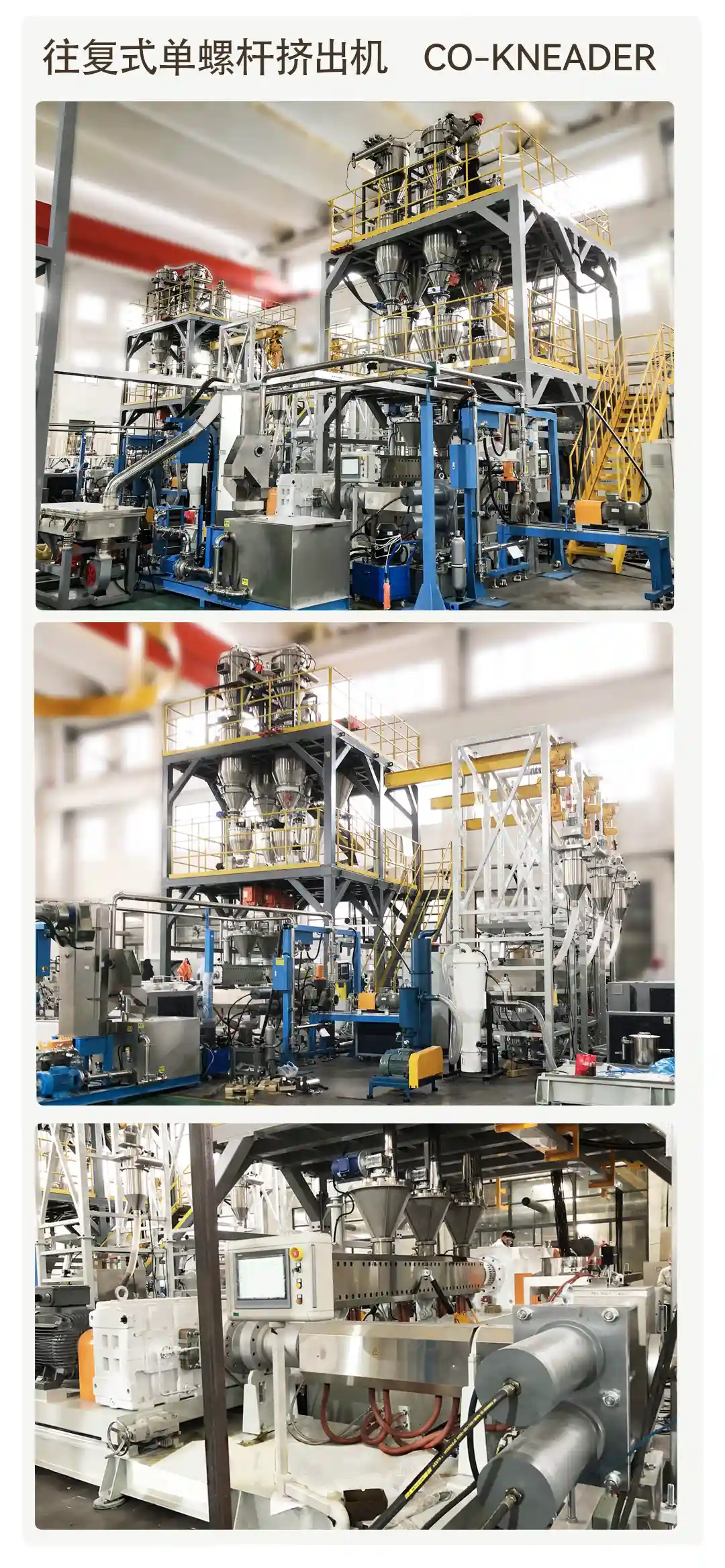
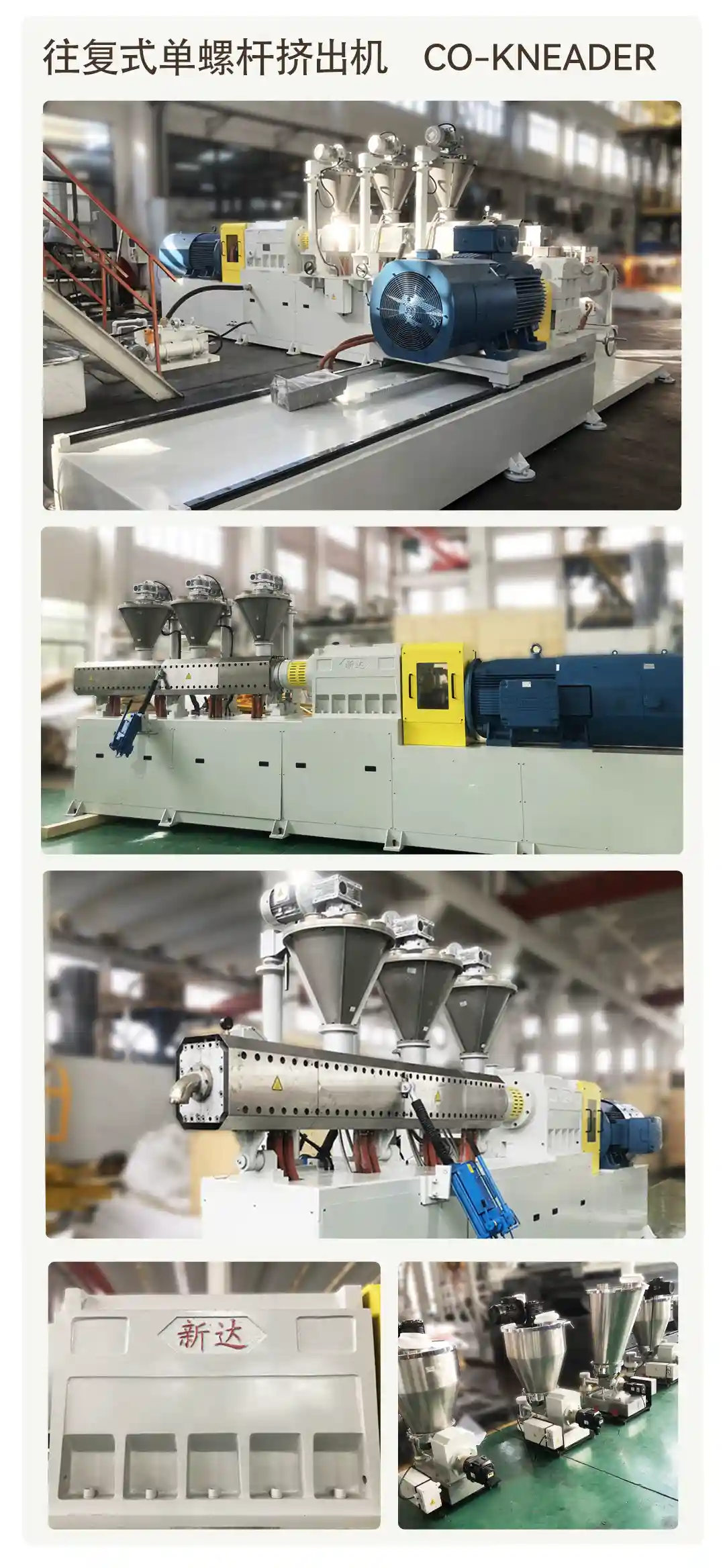
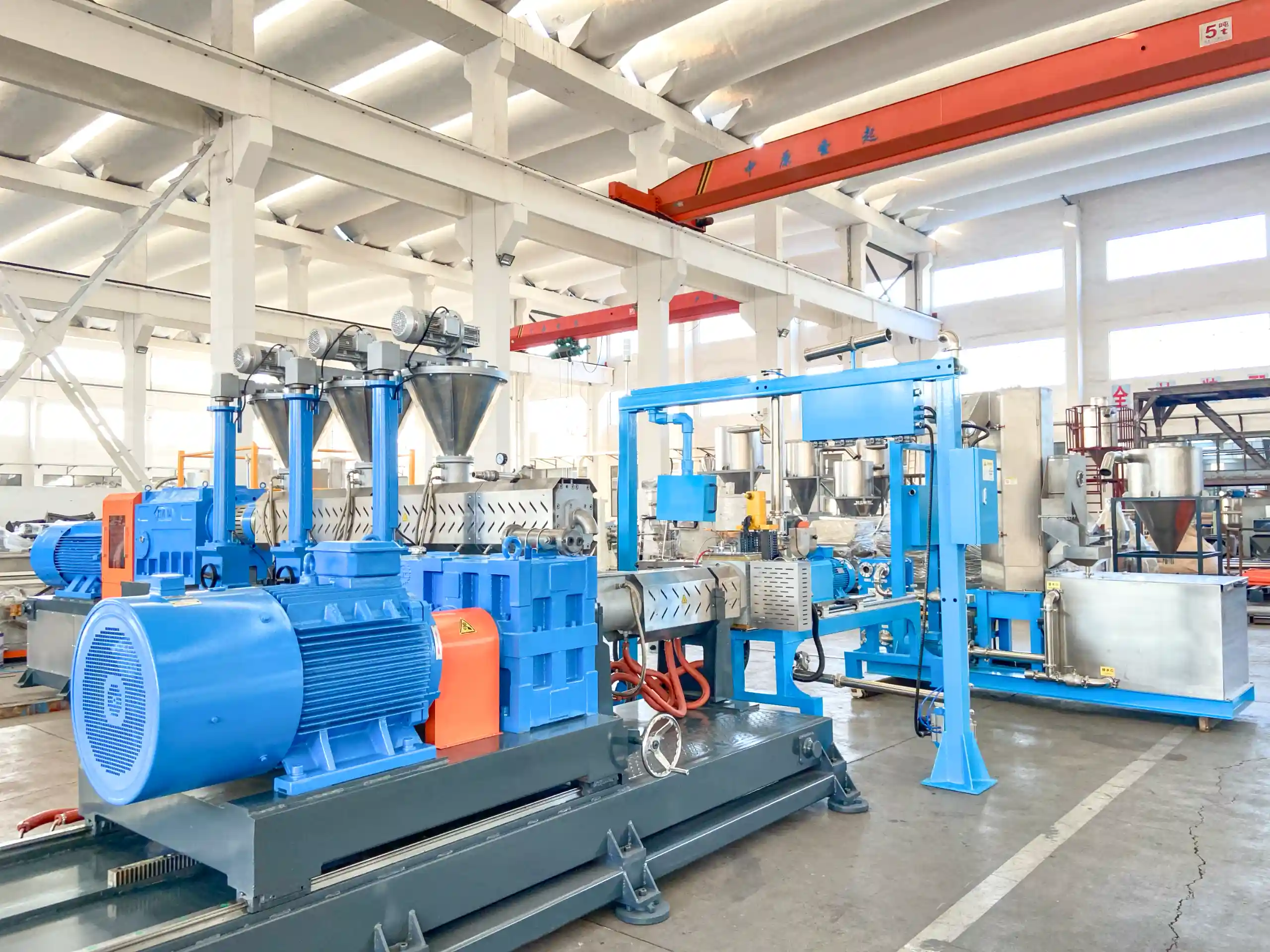
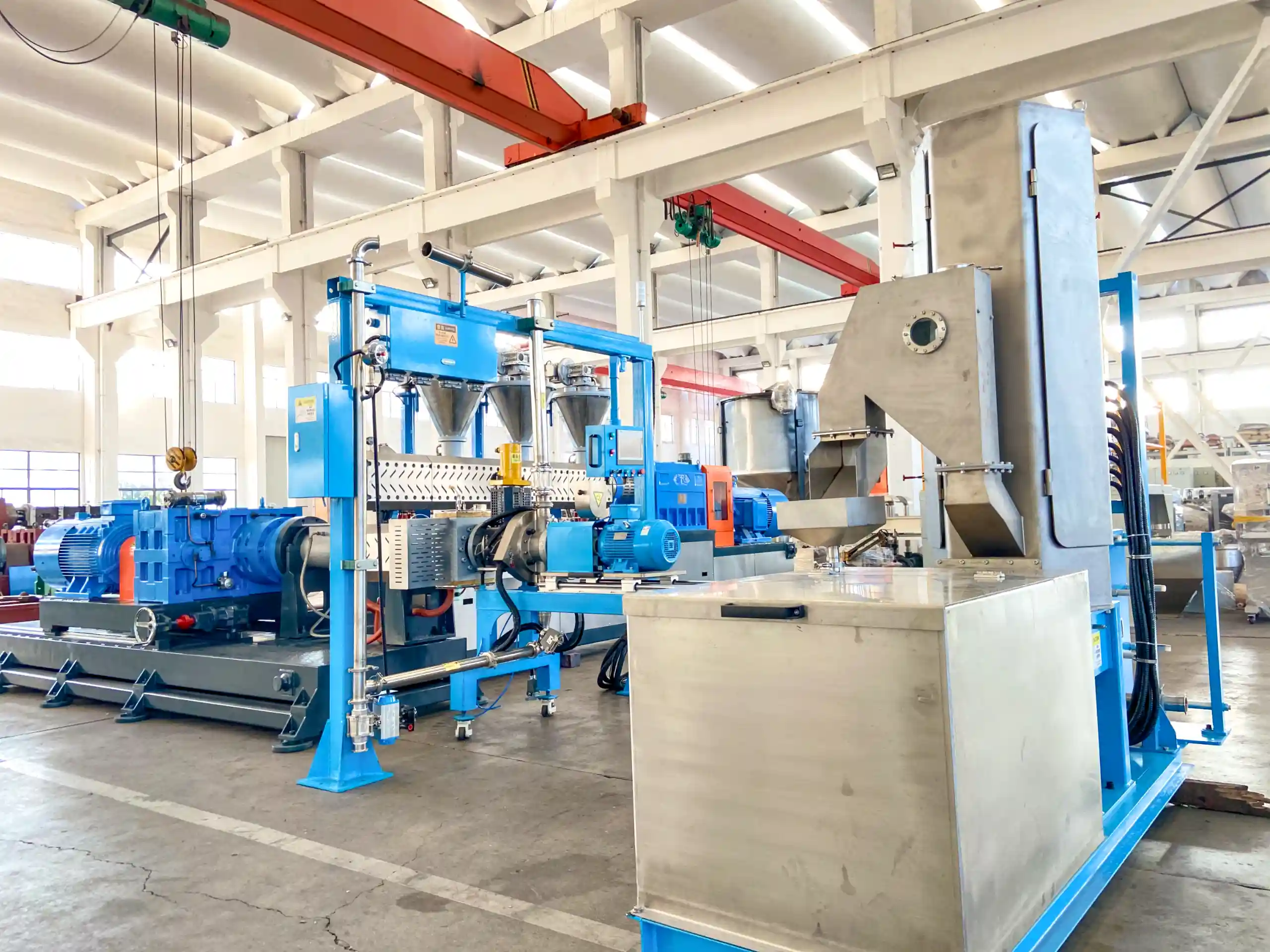
about the extruder
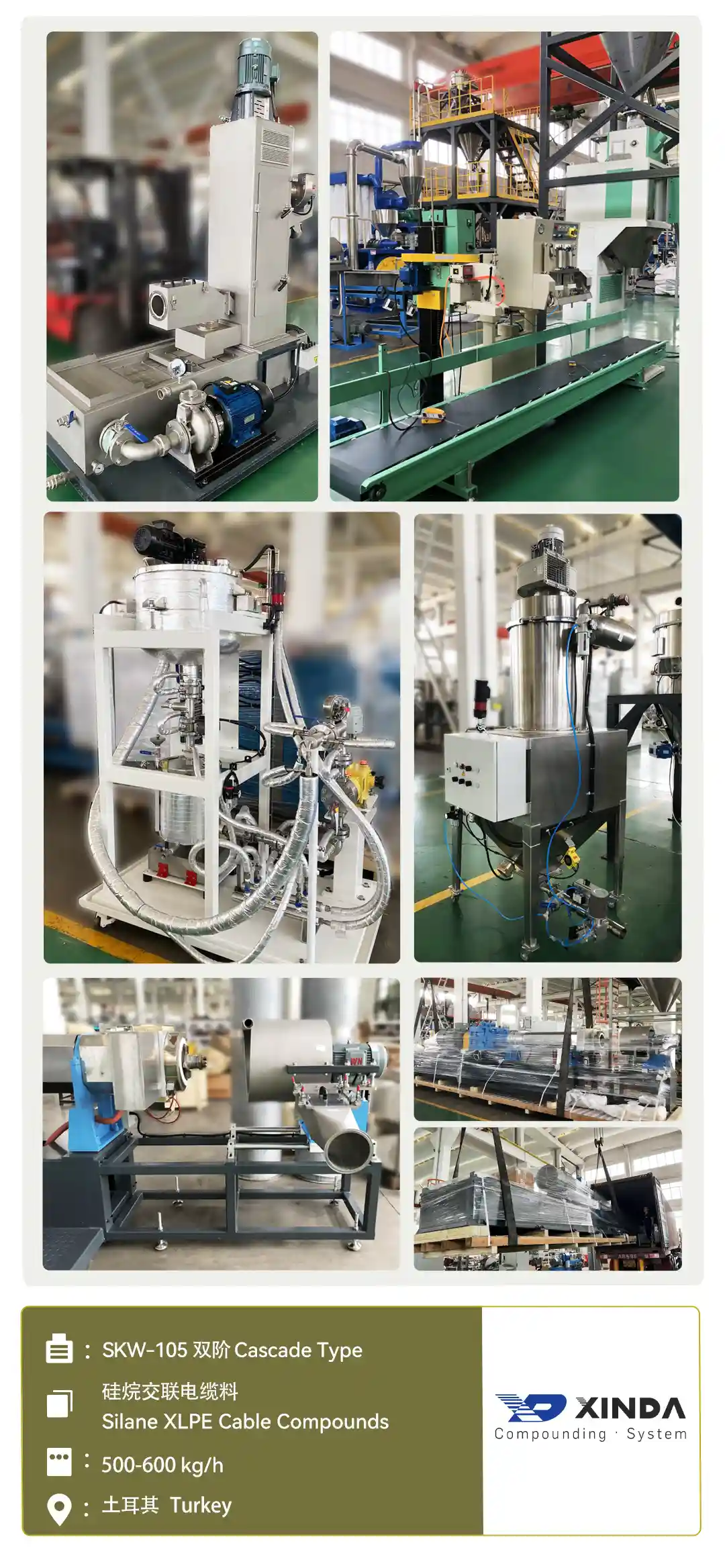
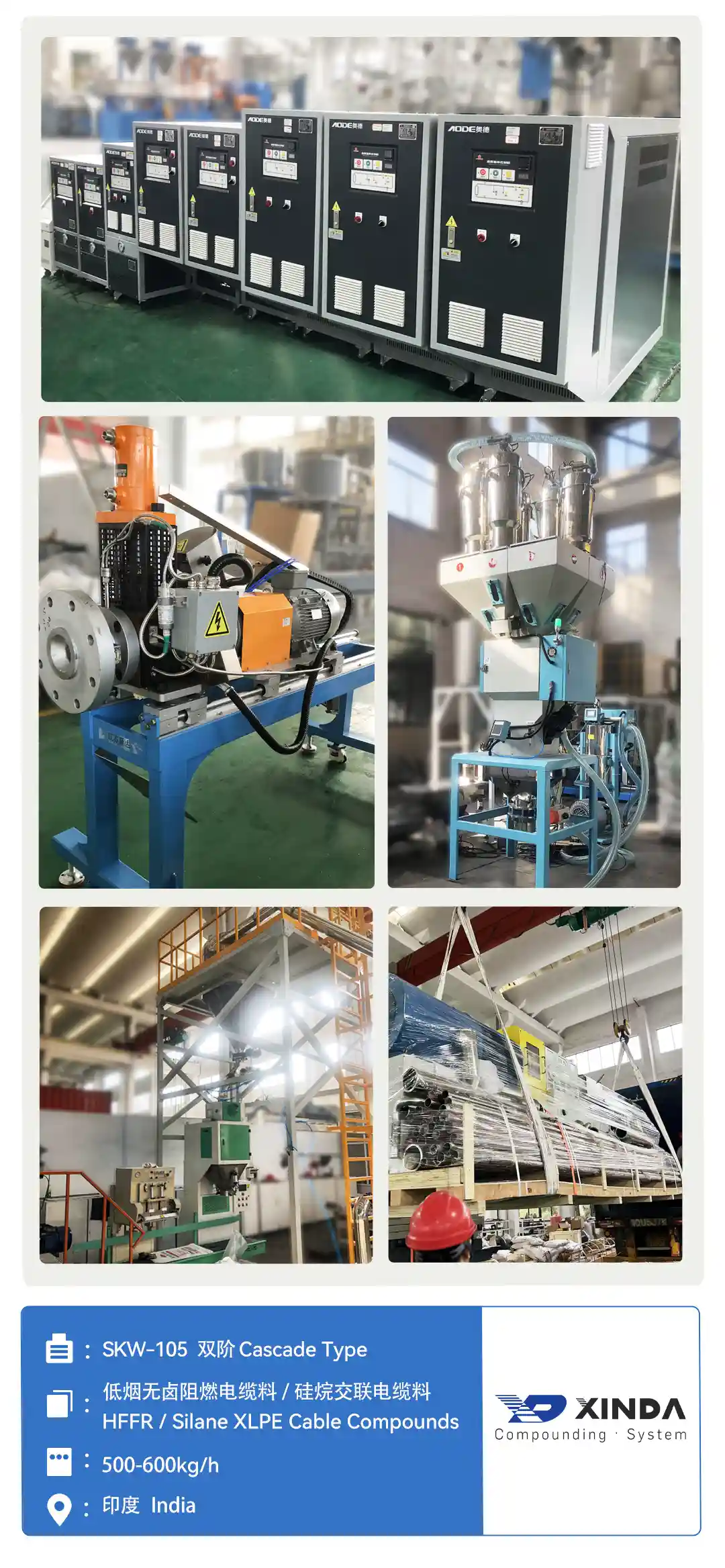
Silane XLPE Cable Compounds
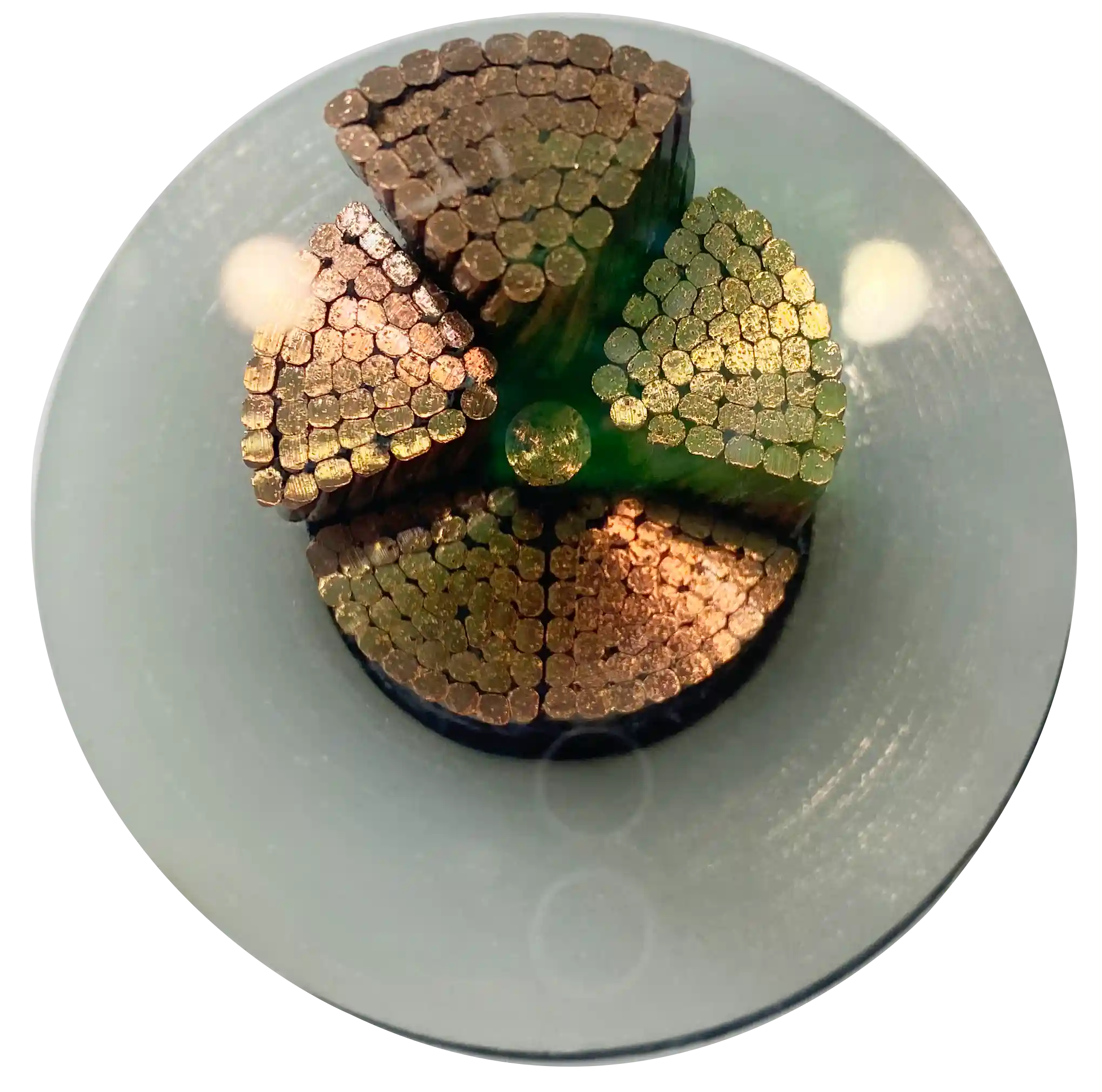
The silane crosslinked cable compounds (also known as sioplas or PEX-B) are now widely used in the wire and cable industry as an insulating material for low-voltage power cables (≤ 10KV). It is a two-step reactive extrusion process. Here we introduce the first step, injecting a silane-peroxide mixture into the melted polyethylene to get a grafted polyethylene. Achieving a high grafting rate depends on the highly distributed dispersion of the compounding system, precise temperature control, and residence time of the material in the extruder.
Product Quality Index
Energy Generation
Processing Steps:
Material handling system-Compounding and extrusion- underwater pelletizer -water cooling system and dryer – Classify – Packing system
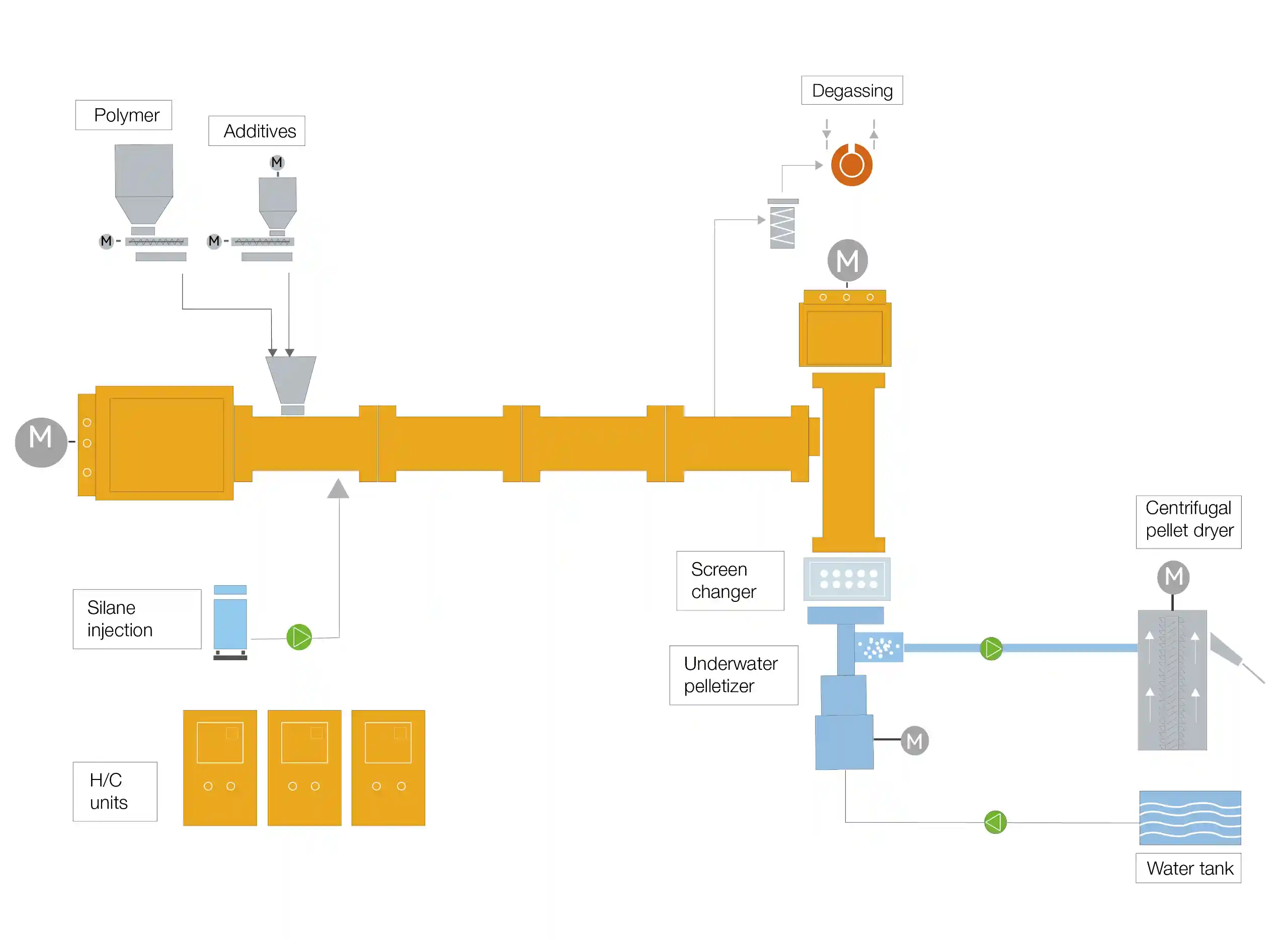
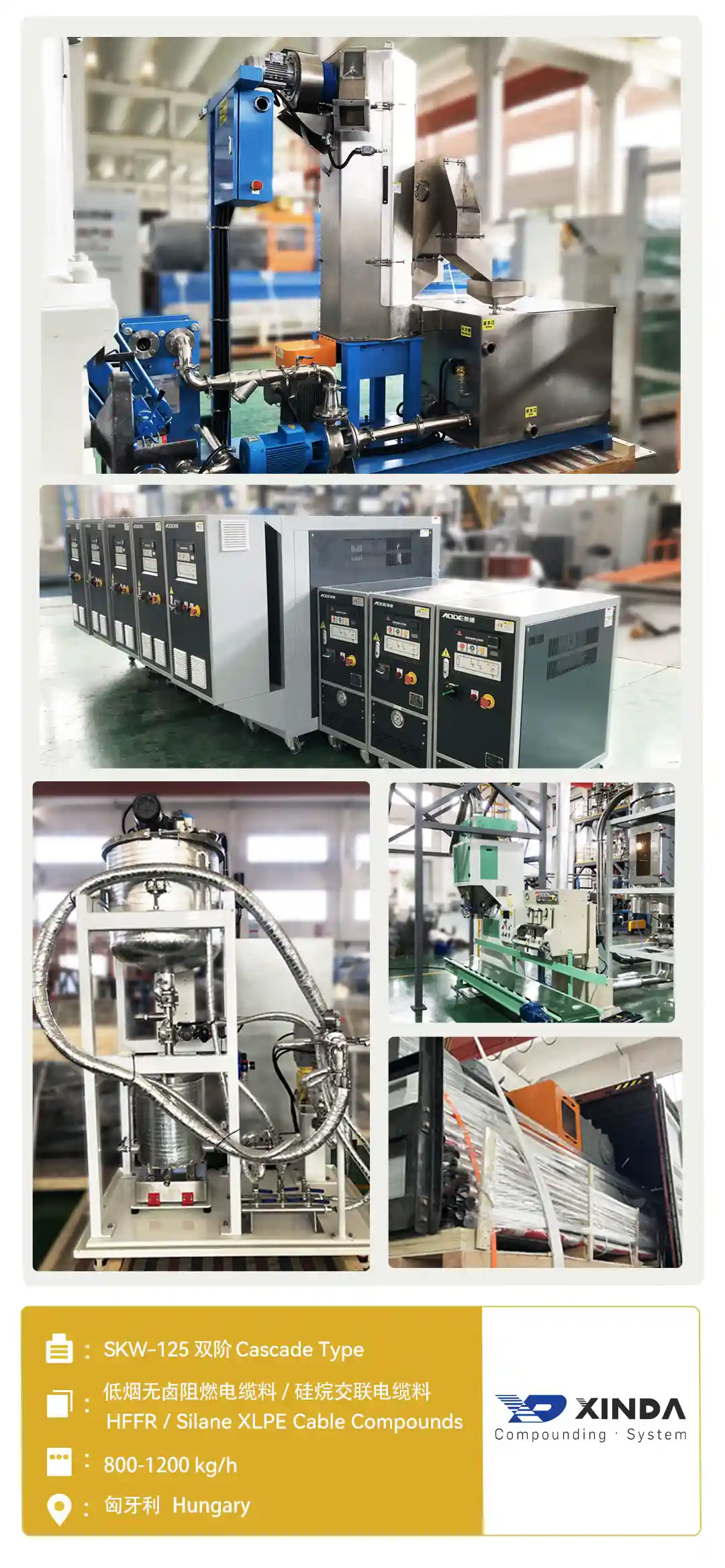
Xinda in Cable Compounding Industry
Xinda Co-Kneader is used by well-known cable companies worldwide, specializing in the production of PVC, HFFR, XLPE, PEX cross-linkable and semi-conductive cable compounds.
Gentle Shearing
Low Process Temperature
Precise temperature control
Flexible Screw Configurations
High Filling Rate of Inorganic Powder
Uniform Distribution of Various Additives
Working Principle
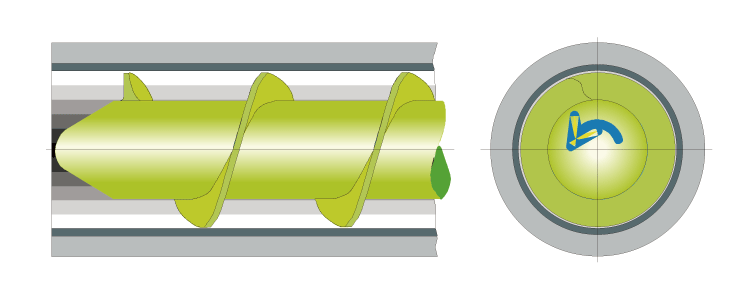
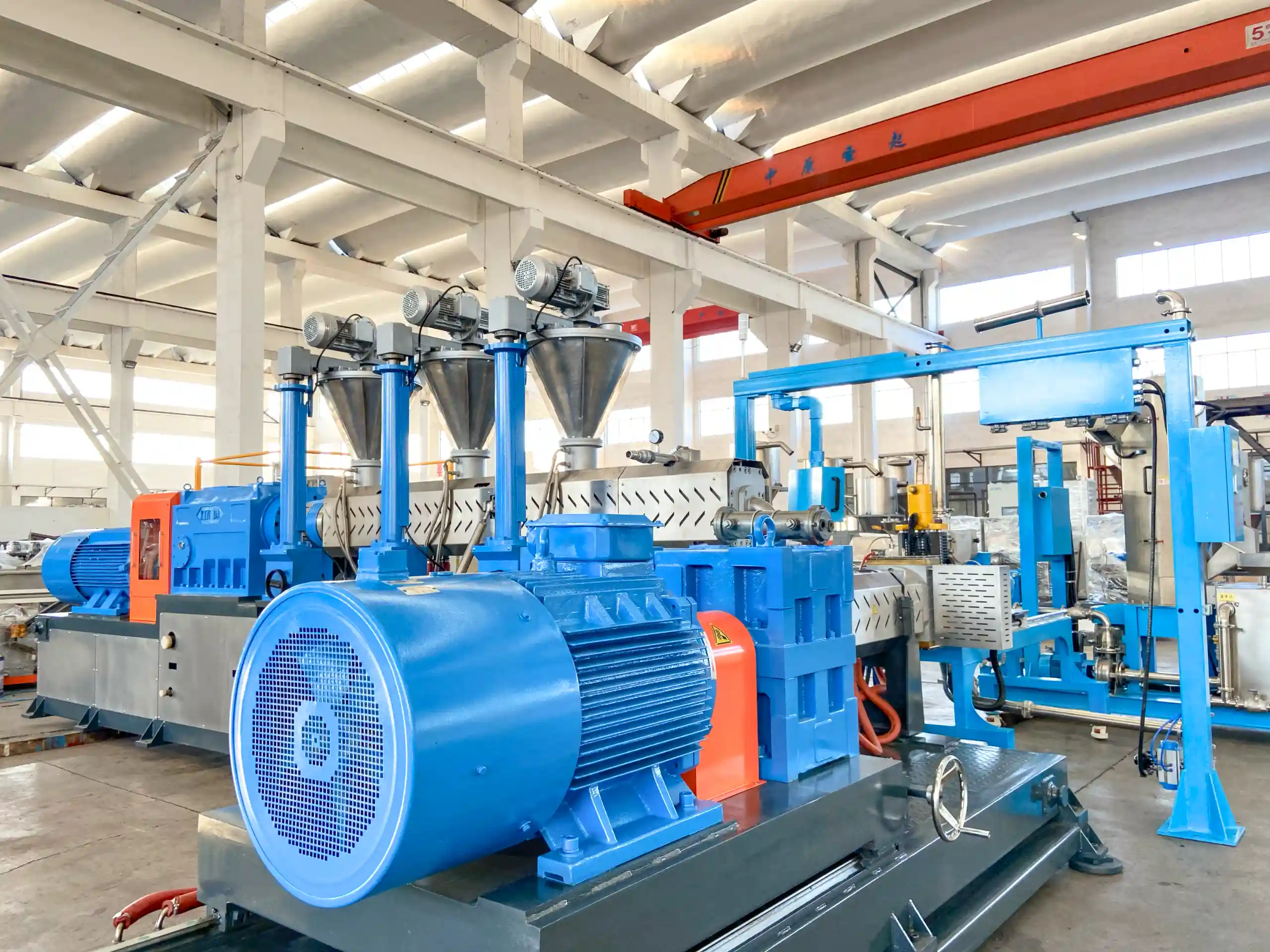
Classic Single Screw
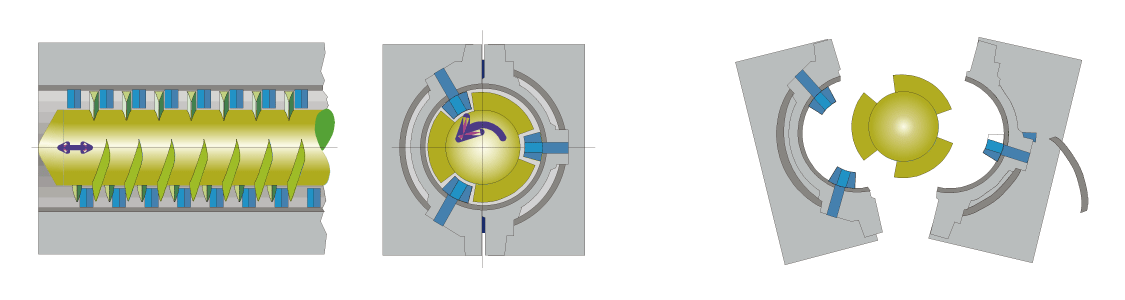
Co Kneader
Liquid Injection System
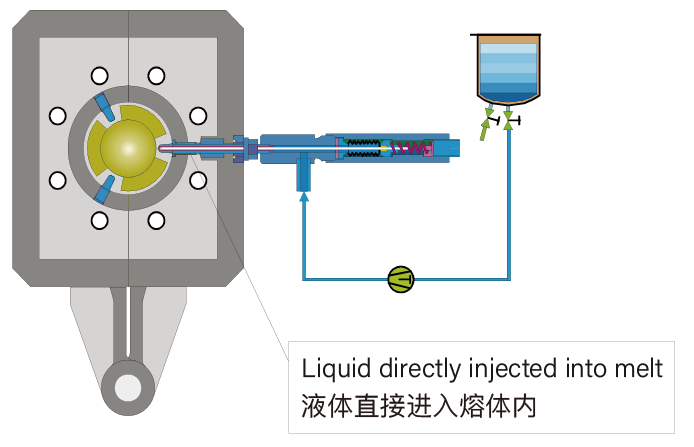
The liquids are directly injected into the melt at the appropriate time and place
The process is extremely accurate, safe and hazard free
There are no losses due to volatilisation and no deposits on metal surface
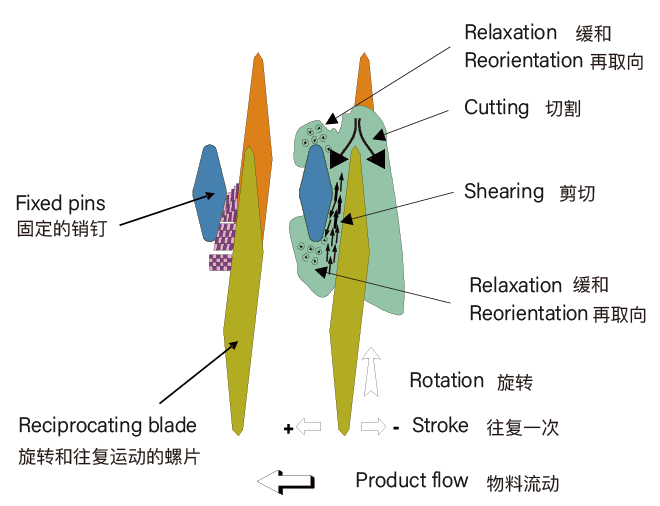
Shear Mechanism in the Co-Kneader
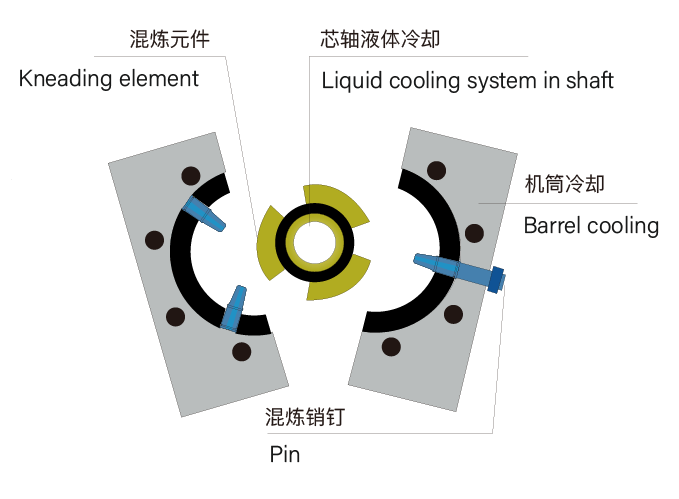
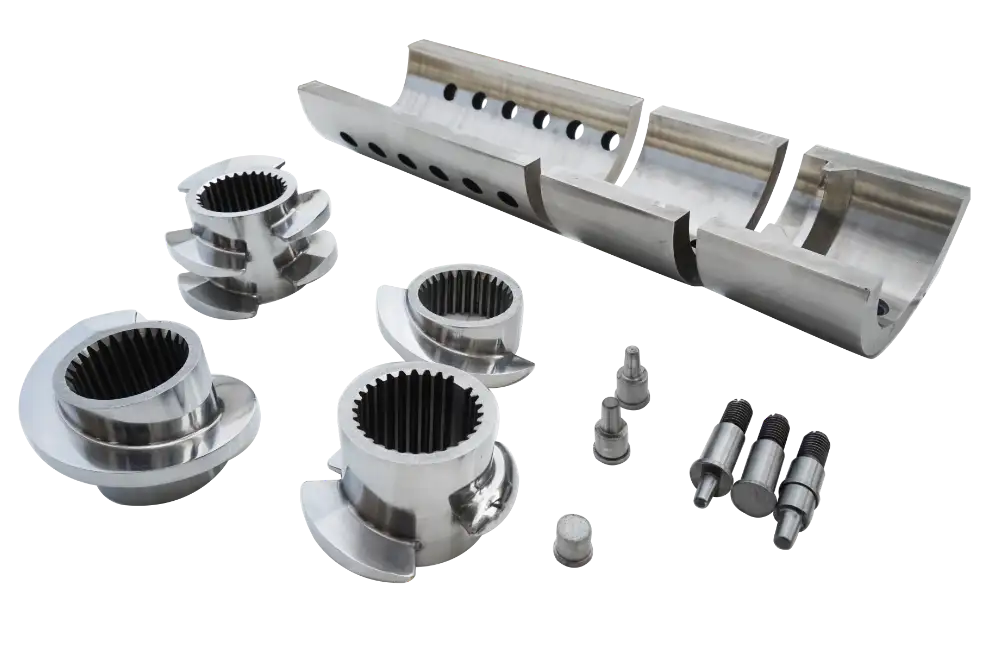
Hollow Pins for Thermocouple
Direct immersion in polymer
Precise melt temperature
Temperature stability of the process
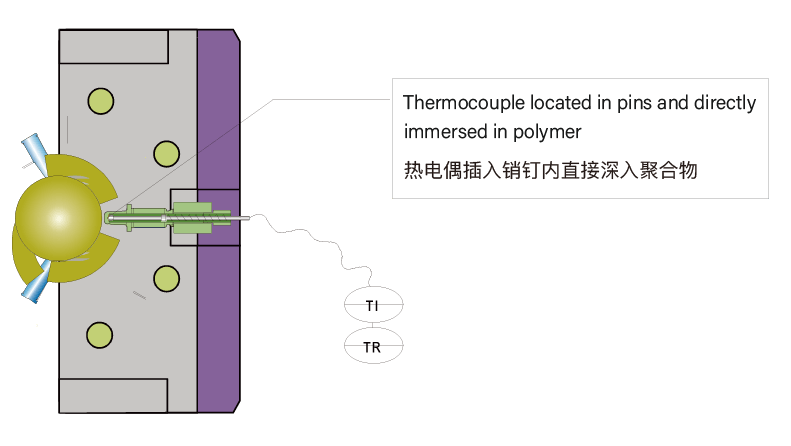
Temperature Control
Barrel: Liquid or electrically heated / Water Cooled
Shaft: Liquid heated/ cooled
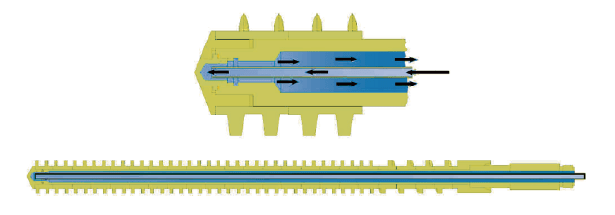
Easy adaptation of screw configuration
The screw consists of individual elements, that can easily be exchanged or replaced